The Cells Alive Animal Cell Worksheet embarks on an enlightening journey into the intricate realm of animal cells, unraveling their remarkable structure, functions, and interactions with captivating detail and precision.
This comprehensive resource delves into the essential components of an animal cell, deciphering the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane as the foundational elements of cellular life. Through meticulously crafted illustrations, learners gain a vivid understanding of the cell’s intricate architecture.
Cell Structure
Animal cells are the basic units of life for all animals. They are composed of various parts, each with its own specific function. The major components of an animal cell include the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains the cell’s genetic material, which is organized into structures called chromosomes. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane that regulates the movement of materials in and out of the nucleus.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell. It contains all the organelles, which are small structures that carry out specific functions within the cell. The cytoplasm also contains the cytoskeleton, which is a network of protein filaments that provides support and shape to the cell.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is a thin layer of lipids that surrounds the cell. It acts as a barrier between the cell and its surroundings, regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
Cell Organelles
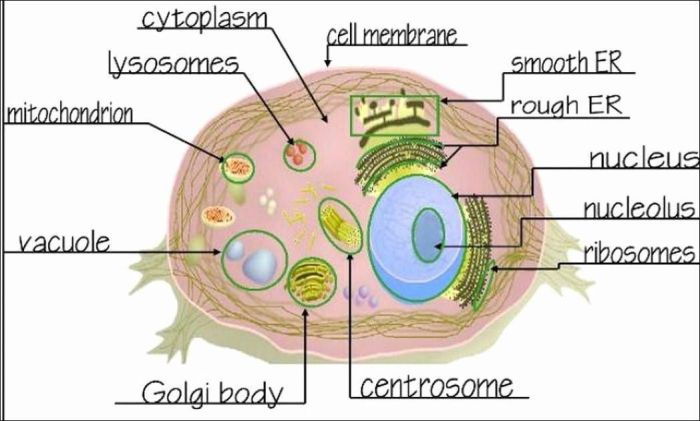
Animal cells contain a variety of organelles, each with its own specific function. The major organelles include the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
Mitochondria, Cells alive animal cell worksheet
Mitochondria are often referred to as the “powerhouses of the cell” because they generate most of the cell’s energy through a process called cellular respiration.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins and lipids. It is divided into two types: the rough endoplasmic reticulum, which is studded with ribosomes, and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, which lacks ribosomes.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion from the cell.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are small, sac-like organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They break down waste products and worn-out cell parts.
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Mitochondria | Energy production |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Protein and lipid synthesis and transport |
| Golgi Apparatus | Protein and lipid modification and packaging |
| Lysosomes | Waste disposal |
Cell Processes
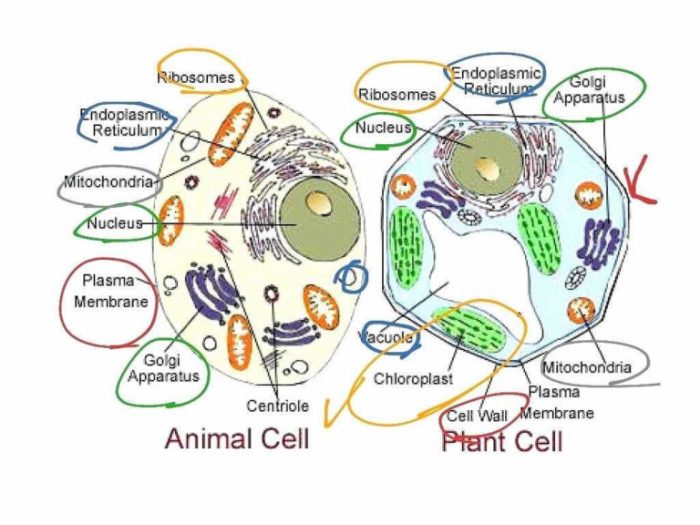
Animal cells undergo a variety of processes, including cell division, growth, and differentiation. These processes are essential for the growth and development of organisms.
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two or more daughter cells. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is used for growth and repair, while meiosis is used for sexual reproduction.
Cell Growth
Cell growth occurs when a cell increases in size and mass. Cell growth is regulated by a variety of factors, including the availability of nutrients and growth factors.
Cell Differentiation
Cell differentiation is the process by which a cell becomes specialized to perform a specific function. Cell differentiation is regulated by a variety of factors, including the cell’s genetic makeup and the environment in which it lives.
Cell Interactions
Animal cells communicate with each other through a variety of mechanisms, including cell signaling and cell adhesion. These mechanisms allow cells to coordinate their activities and respond to changes in their environment.
Cell Signaling
Cell signaling is the process by which cells send and receive chemical signals. Cell signaling can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including direct contact between cells, the release of chemical messengers, and the activation of receptors on the cell surface.
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells attach to each other and to the extracellular matrix. Cell adhesion is mediated by a variety of proteins, including integrins and cadherins.
- Autocrine signaling: A cell sends a signal to itself.
- Paracrine signaling: A cell sends a signal to nearby cells.
- Endocrine signaling: A cell sends a signal to distant cells through the bloodstream.
Cell Applications
Animal cell biology has a wide range of practical applications in fields such as medicine, biotechnology, and agriculture. These applications include the development of new drugs and treatments, the production of genetically modified organisms, and the improvement of crop yields.
Medicine
Animal cell biology is used to develop new drugs and treatments for a variety of diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
Biotechnology
Animal cell biology is used to produce genetically modified organisms (GMOs). GMOs are organisms whose DNA has been altered in a laboratory. GMOs can be used to produce a variety of products, including pharmaceuticals, food, and biofuels.
Agriculture
Animal cell biology is used to improve crop yields. Crop yields can be improved by developing new varieties of crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases.
FAQ Section: Cells Alive Animal Cell Worksheet
What is the significance of the nucleus in an animal cell?
The nucleus serves as the control center of the cell, housing the genetic material (DNA) and directing cellular activities.
How do mitochondria contribute to cellular function?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating energy through cellular respiration.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell?
The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or storage.